Chapter 2 - Principles Of Management
What do you understand by principles of management?
- They are statements of fundamental truth
- They provide guidelines which help management to take decisions and action
- They are derived by observation and experimental studies
- They establish cause and effect relationship
How are management principles derived? – 3 marks
Management principles are derived by observation and experimental studies as follows:
Observation:
Management principles are derived by observing and analysing the events management have to face in actual practice. For example the principle of division of labour was derived after it was observed that dividing the work based on the workers’ knowledge and experience, resulted in improved performance.
Experimental Studies:
By conducting experimental studies. For example – suppose we wish to conduct an experimental study to confirm the correctness of the principle of unity of command which states that no subordinates should receive orders from more than one boss, we take two groups of employees – one having only one boss and the other having two bosses. After some time it will be noted that the group with one boss is doing better than the other. This confirms that the principle of unity of command is correct.
State any 3 reasons why proper understanding of management principles is necessary?
Or
Explain briefly any 3 points establishing the NEED/IMPORTANCE of management principles?–3 marks Marking Scheme
Management principles are needed for the following reasons: (OCE)
Optimum use of resources:
The management principle of “science, not rule of the thumb” suggest that every task should be done with minimum effort and energy and additional work can be done with the saved energy. By saving time, efforts and energy activities can be made economical and enhance the productivity of the resources.
Change in technology:
The management principle of “division of labour” helps management in identifying in which activity technology has changed. If there is no division of labour then confusion may prevail about what and how much to change and the firm might find it difficult to face competition and might in extreme case run out of business.
Effective Administration:
-
- The principle of ‘scalar chain’ helps the enterprise to communicate with people at different levels
- ‘Unity of direction’ removes confusion in minds of employees; and
- ‘Unity of command’ avoids dual subordination.
- Thus these principles help management in managing their organisations effectively.
- Besides the above, management principles also provide guidelines to managers to:
- Effectively handle complex problems.
- Clearly understand the nature and scope of their work
- To make optimum use of the resources.
- To take scientific decisions to meet changing conditions.
Explain 3-4 points that highlight nature/characteristics of principles of management –3 or 4 marks
The following characteristics highlight the nature of management principles: (FUEL)
Flexibility:
Management principles are flexible guidelines and can be modified in different ways in different situations depending upon the knowledge and experience of an employee and importance of decisions that have to be taken.
Universal application: Taylor’s techniques of mgt are UNIVERSALLY APPLICABLE. Do you agree? Give any four reasons in support of your answer – 4 marks
· Management principles are effective in:
o Both business enterprises as well as government organisations. (All social, economic, political, cultural or even religious organisations apply management principles for the successful operations of their activities)
o All types or sizes of organisation
o All types of problems
o Any type of group action be it the army unit, hospital, etc
· Example: Delegation of authority in any nature of business is considered as key to organisational success universally because it empowers people to take decisions on the spot.
· Hence it can be concluded that the principles of management are universal and it is possible to transfer them from one organisation to another and from one country to another.
Evolutionary:
Management principles are developed either from organised quantitative facts or from long experiences of leaders and scholars of management thoughts. Therefore they are evolutionary in nature.
Limited application:
Application of principles of management in real life is affected by certain limiting factors such as nature, size, form of business, etc.
An organisation follows the principles of management. Learn the
(a) principles
(b) positive effects, or (c) adverse effects and
(c) examples if any of
each of the following principles of management on the organisation? – 3 marks
Which principle of management is violated if subordinate is asked to receive orders from two seniors? Explain with a suitable example. Name any two ADVERSE EFFECTS that may take place due to this violation - 4 marks CBSE, 2005
Fayol’s principle of UNITY OF COMMAND is violated. This principle implies that an employee should receive orders from only one superior. If he gets orders from more than one superior at a time then he will be confused as to which superior’s orders should be carried out first.
Adverse Effects: If this principle is violated it may lead to confusion, indiscipline, delay in performance, difficulty in satisfying seniors and difficulty in fixing responsibility. Therefore to avoid this confusion, dual subordination should be ruled out.
Example: If a salesman gets instructions from marketing as well as production department at the same time. He may get instructions from production manager to go slow in selling the product as there is a power cut in the factory and goods are not being produced fast enough.
On the other hand the marketing manager may insist he sell as per schedule to reach the target. In such a situation, it may be difficult for the salesman to carry out the orders of two
people, as their instructions are contradictory. Unity of command therefore helps in avoiding such contradictory issues.
Which principle of management envisages that each group of activities having the same objectives must have one head and one plan? Explain the principle with a suitable example. What are the positive effects of this principle – 3 marks
UNITY OF DIRECTION
- This principle calls of “one manager one plan” for a group of activities having the same objective so that the efforts of all employees are directed towards common goals.
- The positive effect of this principle is that it ensures unity of action and facilitates coordination.
- Example: Suppose an automobile company has three divisions – cars, scooters and three wheelers. Now each division must have its own targets since each product has its own market and problems. Each division must plan its target as per its environmental conditions to achieve better results.
(I mark for naming the principle + 1 mark for each point of explanation + 1 mark for example)
What do you mean by the principle “ SUBORDINATION OF INDIVIDUAL INTEREST TO GROUP/GENERAL INTEREST” CBSE-2005 Set 1. 3 marks
According to this principle of Fayol, management should reconcile the interest of an individual with those of the group. However if they differ, then the group interest should supersede that of the individual interest.
Example: If a manager gets an order for supply of a product at his own initiative and due to which the company benefits immensely.
Positive Effect: The principle suggests that the profit should be shared by all since one person cannot alone meet an order.
State the principle of ESPIRIT DE CORPS? What is the positive effect of this principle? – 3 marks (CBSE-2000, CBSE-2005 Set 1)
- Espirit de corps means “spirit of cooperation”.
- It means harmony, mutual understanding and team spirit among workers.
- If there is team spirit, everyone comes forward to help others.
- It helps to develop an atmosphere of mutual trust and understanding and a sense of belong among workers, which inspires them to work harder and improve quality of work.
- Employees up to the standard should be rewarded and those who are not up to the standard should be given an opportunity to improve their performance.
- Positive Effect: When esprit de corps is present the need to penalise the defaulting person is minimised
Explain FAYOL’S Principle of DIVISION OF WORK (2 marks)
State the adverse effects on the violation of the principle of division of work – V. Imp
· According to this principle of Fayol’s, every task should be divided into small task and assigned to the right person who is capable of doing that job. He should also be trained for doing that job. This is called division of labour.
· This principle applies to all kinds of work managerial as well as technical
· Positive Effect: A person holding the same post and doing the same job will over time specialise in that job and improve his performance, efficiency and result in increased output.
· Adverse Effects: If this principle is violated it leads to
(a) inefficiency (b) delay in work (c) increase in costs (d) decrease in output.
Explain FAYOL’S PRINCIPLE OF DISCIPLINE (2 marks)
- According to Fayol, discipline means respect for agreements that are directed at achieving energy, application, obedience and outward mark of respect (EARO).
- Fayol says that discipline requires:
- Good supervisors at all levels
- Agreements should be clear and fair
- Penalties should be fairly imposed
- However Fayol does not support wrong use of authority to enforce discipline such as warnings, fines, suspensions, dismissal, etc.
- Example: If a company has entered into agreement with employees regarding their wages for 5 years then the company should honour it. Likewise, employee should also honour the commitments made by them.
An organisation follows the principles of management. What are the POSITIVE EFFECTS of each of the following principles of management on the organisation (3 will be asked) -3 marks (30-40 words)
(a) Unity of Direction
Positive effect: of this principle is that it ensures unity of action and facilitates coordination
(b) Espirit de corps
Positive Effect: When esprit de corps is present the need to penalise the defaulting person is minimised
(c) Subordination of individual interest to general interest
Positive Effect: This principle suggests that the profit should be shared by all since one person cannot alone meet an order.
(d) Scalar chain
Positive Effect: This will produce quicker results in sorting out problems in one or two sittings and avoid lengthy time procedure, danger of miscommunication, distortion or even danger of being killed in the process.
(e) Equity
Positive Effect: If similar treatment is assured to people performing similar jobs and the management is always kind, fair and just in its dealing with its subordinates, it earns the respect, loyalty and devotion of the employees and they are motivated to put in their best efforts.
(f) Division of work:
Positive Effect: A person holding the same post and doing the same job will over time specialise in that job, improve his performance, efficiency and result in increased output
An organisation follows the principles of management. What are the ADVERSE EFFECTS of each of the following principles of management on the organisation?
(a) Unity of command
Adverse Effect: If this principle is violated it may lead to confusion, indiscipline, delay in performance, difficulty in satisfying seniors and difficulty in fixing responsibility. Therefore to avoid this confusion, dual subordination should be ruled out.
(b) Unity of order
Adverse Effect: When there is no arrangement for things and people, the organisation will not be able to achieve its objectives in time. Effective utilisation of physical and human resources will not be possible.
(c) Stability of tenure of personnel
Adverse Effect: If this principle is violated, it will lead to high labour turnover rate and will increase the cost of selection and training of the employees
(g) Division of work
Adverse Effects: If this principle is violated it leads to
(a) inefficiency (b) delay in work (c) increased costs (d) decreased output.
(h) Remuneration of personnel
Adverse Effects: If fair remuneration is not paid to the workers, it will create a sense of dissatisfaction among workers leading to various problems such as trade unions, strikes, high labour turnover rate, etc
Explain Fayol’s view on REMUNERATION OF PERSONNEL? – 2 marks
- In Fayol’s view, remuneration of employees should be fair and reasonable which will satisfy both employers and employees.
- It will stimulate the workers to work more and better.
- Wages should be determined on the basis of
- work assigned
- cost of living
- financial position of the business; and
- average wage rate for similar work in the industry.
- Adverse Effects: If fair remuneration is not paid to the workers, it will create a sense of dissatisfaction among workers leading to various problems such as trade unions, strikes, high labour turnover rate, etc.
Why did Fayol suggest the idea of ‘GANG PLANK’? What light does it throw on the nature of Fayol’s principles? – 5 marks
Or
Illustrate SCALAR CHAIN with suitable example? 3 marks
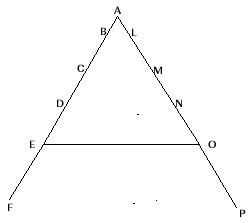
Fayol's Scalar Chain
- According to Fayol, scalar chain is a chain of superiors ranging from highest to lowest rank of authority.
- Under normal circumstances every communication should follow the proper channel and pass through every link in the scalar chain.
- Example: The above figures shows the scalar chain linking mangers at lower levels with top management. If E wants to make contact with O for some work he has to move through a long route i.e. D, C, B, A, L, M, .N and finally to O without breaking the chain of command. This will cost lots of time of E.
- Positive Effect : In case of urgencies however, the prescribed route can be violated and gang-plank (direct contact) between the two concerned authorities may be established. This will produce quicker results in sorting out problems in one or two sittings and avoid lengthy time procedure, danger of miscommunication, distortion or even danger of being killed in the process.
- The idea of gang-plank throws light on the flexibility of Fayol’s principles.
What is GANG-PLANK? Show it through a diagram – 3 marks
Gang-plank is the technique of shortening the route of communication which is usually followed through all channel of hierarchy. Fayol suggested that in case of urgencies, by jumping the prescribed line of authority, these officials could deal with one another at one sitting and sort out several problems quickly.
How can Fayol’s PRINCIPLES OF EQUITY and order be applied in work situation?-4 marks. Illustrate with an example. (CBSE-1996, CBSE-2001)
Or
Which principle of management aims at securing the loyalty and devotion of the employees by giving them kind, fair and just treatment? Explain this principle with a suitable example -4 marks
- The principle of equity suggest that similar treatment is assured to people performing similar jobs. Example – two typists should be paid the same wage rate.
- An effective management is always kind, fair and just in its dealing with its subordinates. This way it earns the respect, loyalty and devotion of the employees and they are motivated to put in their best efforts.
- However the principle of equity should be applied at all levels. Workers should be treated at par at every level.
- For example: There should be no discrimination with regards to position, sex, age etc while granting medical leave to the employees.
Name the function of management, which concentrates on employing and retaining the right person at the right place. Explain why this function is important in any organisation.
Or
If an organisation does not provide the right place for physical and human resources in the organisation., which principle is violated? What are the consequences of it?
Principle of ORDER:
If an organisation does not provide the right place for physical and human resources in the organisation, the PRINCIPLE OF ORDER is violated.
The principle of order is concerned with proper arrangement of things and people. This principle can be divided into two:
Material order: An orderly arrangement of things is called material order. There should be an orderly arrangement of physical factors of production like land, raw material, tools and equipment. This means that there should be a specific place for everything. Every piece of land and every article should be used properly, economically and in the best possible way.
Social order: An orderly arrangement of people is called social order. This includes employees. Right man for the right job will ensure effective use of man power resources. Right place for everything and for everyone should therefore be the guiding principle for every management.
Adverse Effect: When there is no arrangement for things and people, the organisation will not be able to achieve its objectives in time. Effective utilisation of physical and human resources will not be possible.
Explain the principle of “INITIATIVE” through a suitable example - 3 marks (CBSE-2000)
- Freedom to think and execute a plan is known as initiative.
- Employees at all level should be allowed to take initiative in work related matters.
- Encouraging initiative is likely to motivate employees to work better and harder.
- However initiative should not be confused with disrespect to authority. For example: if any employee is given the initiative to make suggestions but once the decision is taken on any issue then there is no scope for disobedience.
Fayol points out the danger and costs of unnecessary labour turnover in one of his principles. Name and explain the principle.(CBSE-2000) (2004)
Or
Illustrate the principle of “STABILITY OF TENURE” through a suitable example – 3 marks
Fayol emphasised in his principle “STABILITY OF TENURE” that employees should not be shifted from their position frequently. The period of service should be fixed. It takes time for an employee to get used to his work and he cannot render useful service if he is removed before he gets accustomed to the work assigned to him.
· Production requires team-work. If the members of the team go on changing the entire production process will be disturbed.
· An effective management will ensure that trusted, trained and experienced personnel do not leave the organisation, unless it is unavoidable such as illness, retirement or death of an employee.
· Stability of job creates a sense of belonging among the workers and so they are motivated to improve the quantity and quality of work.
•Adverse Effect: If principle of stability of tenure is violated, it will lead to high labour turnover rate and will increase the cost of selection and training of the employees.
Define Scientific Management? – 2 marks
- According to F.W.Taylor who is regarded as the father of scientific management, “Scientific Management is the art of knowing exactly what you want your men to do and seeing that they do it in the cheapest way”.
- It means conducting business activities according to standardised tools, methods and trained personnel in order to increase the output, improve its quality and reduce cost and wastage.
Explain any two principles of Scientific Management.
Or
Describe in brief TAYLOR’S PRINCIPLES of (i) science not rule of the thumb and (ii) separation of planning and operational work - 4 marks.
Science not rule of thumb – 2 marks
- In traditional management “rule of thumb” was prevailing. This was also known as “Trial and errors method “ or “Hit or miss method”
- This principle meant that go on trying, failing and wasting the resources and finally perfecting the job.
- Workers were careless because no specific amount of work was expected from them. Even the employer did not know the real worth of his employee. Everything was left to ”Trial and Errors” method.
- Taylor introduced the scientific method in which he emphasized that “Rule of the thumb” does NOT involve thinking before doing and that each job in the organisation should NOT be performed based on intuition, experience and hit and miss methods.
- According to scientific method the causes, effects and exact measures of effort and output should be kept in view for any work to be performed. This forms the core of scientific management.
Separation of planning and operational work: - 2 marks
- According to Taylor, planning operations should be separated from operational operations.
- He stressed that managers should concentrate on planning the job of the workers while workers’ potential should be developed to the fullest extent for their own benefit as well as the prosperity of the company.
- For this purpose there has to be a scientific selection of workers and they should be trained to adopt new methods of work.
Harmony not discord -2 marks
- According to Taylor those who work together should work in harmony i.e. there should be mutual give and take and proper understanding among the managers and workers. This is because group efforts contribute more than an individual’s efforts.
- Managers should adopt an enlightened attitude and share the productive gains with the workers and workers on their part should work with discipline and loyalty.
Maximum not restricted output – 2 marks
- Continuous productivity is one of the principles of scientific management.
- According to this principle, production should not be curtailed and management and labour should both be interested in increasing productivity.
- Conflict between management and labour arises mainly on division of surplus. The best solution is to increase the size of the surplus so that both can have a larger share.
Cooperation not individualism: - 2 marks
- Scientific management works on cooperation between workers and management and among workers themselves.
- Management can earn higher profits if workers produce better quality, low cost goods.
- Workers can earn higher wages if management provides standard materials, standard tools, standard working conditions and training in standard methods.
Explain “method study” as a technique of Scientific Management? –2 marks (CBSE-2004)
- Method study is concerned with methods of performing a job.
- There are various methods to perform the same job with different costs requirements. Taylor suggested that management should find out one best way to perform the task.
- For example – The methods of manufacturing shoes may be manual or mechanical but the cost of labour and capital to manufacture shoes according to each method may vary. Management has to decide which method to use before it starts manufacturing.
- The objective of method study is to minimise production costs by a proper mixture of factors of production in order to achieve desired result.
- Method study should be done right at the planning stage of the job.
What role do” motion studies” play in setting the standard task? – 2 marks
- Motion study is the technique that closely observes the movement of the body/machines required to perform a job so that unnecessary movements can be eliminated and the best way of doing a job is determined.
- Upon a close examination of body’s wasteful motions it is possible to find
- which motions are productive
- which are unproductive
- which motions are incidental i.e. going to the store
- Through motion study Taylor was able to design suitable tools & equipment and educate workers on their use.
Define “fatigue study” on the basis of meaning and purpose? – 2 marks
- Fatigue study helps in setting the time interval and frequency of rest period in completing a task.
- A person will be tired and less productive if he works without rest interval for a long period of time. If he is allowed rest intervals he will regain stamina and work with increased efficiency.
What is the role of “time study” in setting the standard task or help to improve the efficiency of workers.? Give two points in support of your answer? – 2 marks
- Time study measures the standard time taken for a qualified worker to perform a well -defined job.
- Time study is done with the help of a time measuring device.
- Objective of time study is to:
- Determine number of workers to be employed
- Determine cost of labour
- Frame suitable incentive schemes
- Benefit of time study:
- It helps to determine the fair days work of an employee
- It creates time consciousness in a worker
- It eliminates idle time
- It helps in reducing costs
Distinguish between Time Study and Motion Study – 3 marks
|
TIME STUDY |
MOTION STUDY |
|
It measures the standard time taken for a qualified worker to perform a well defined job. |
It studies movements of body/machine to perform a job |
|
The purpose is to decide how much time is normally required to perform a certain job |
The purpose is to avoid wasteful motions and to determine the best way of doing a job |
|
It measures the work provides a yardstick to decide between efficient and inefficient workers |
It eliminates and reduces wasteful and useless motions. |
What is “ Mental Revolution” – 2 marks.
- According to Taylor, mental revolution means that both workers and management should completely change their attitude regarding relation between themselves and their work.
- Management and workers usually suspect each other and try to trick each other.
- Workers all the time feel that management exploits them by extracting a lot of work from them and paying meagre wages. Management on the other hand feels that workers always grumble about the workload and deliberately slow down their work, damage equipments, tools and show indifference to quality of products.
- Mental revolution requires that such a feeling of suspicion or prejudice should be rooted out.
- Management should provide good working conditions and resolves all problems scientifically. Similarly workers on their part should work with discipline and loyalty.
- Instead of fighting for dividing the surplus profit, management and workers should cooperate to increase it.
Do you agree with the view that Taylor’s principles of scientific management and Faylor’s principles of management are mutually complementary. Give any 4 reasons. (3-4 marks)
Or
List 4 distinctions between Fayol’s contribution and Taylor’s theory (Important) 3-4 marks
Yes, they are mutually complementary since no organization can function effectively without mutual cooperation of managers and employees.
The comparative evaluation of their contributions is given below. (FEES)
Focus:
· Taylor tried to improve the productivity of workers and eliminate all kinds of wastes.
· Fayol tried to develop the principles to ensure better management.
Emphasis:
· Taylor’s principles were more applicable at shop level with emphasis on tasks of workers and supervisors.
· Fayol’s principles were more applicable at general management level with emphasis on efficiency of managers and administration
Expression:
· Taylor used the expression “scientific management”
· Fayol used the expression “general theory of administration”.
Starting point:
· Taylor wanted to improve the efficiency of lowest level and then move upwards while formulating the principles of scientific management.
· Fayol began from the top level and moved downwards with emphasis on “unity of direction, command and coordination.