CBSE Board Question Paper Class X - 2009
SCIENCE (Theory)
SET-3
[Time allowed: 2 1/2 hours] [Maximum marks: 60]
General Instruction:
(i) The question paper comprises of two sections. A and B. you are to attempt both the sections.
(ii) All questions are compulsory.
(iii) There is no overall choice. However, internal choice has been provided in all the three questions of five marks category. Only one option in such questions is to be attempted.
(iv) All questions of Section A and all questions of Section B are to be attempted separately.
(v) Questions number 1 to 6 in Section A and 17 to 19 in Section B are short answer type questions. These questions carry one mark each.
(vi) Questions number 7 to 10 in Section A and 20 to 24 in Section B are short answer type questions and carry two marks each.
(vii) Questions number 11 to 14 in Section A and 20 to 24 in Section B are also short answer type questions and carry three marks each.
(viii) Questions number 15 to 16 in Section A and 25 to 26 in Section B are long answer type questions and carry five marks each.
SECTION – A
Q1. Name a reducing agent that may be used to obtain manganese from manganese dioxide. [1]
Q2. Balance the following chemical equations: [1]
![]()
Q3. Why does tooth decay start when the pH of mouth is lower than 5.5? [1]
Q4. Why does sky look blue on a clear day? [1]
Q5. Why does a ray of light bend when it travels form one medium into another? [1]
Q6. Take down this diagram onto your answer book and complete the path of ray. [1]
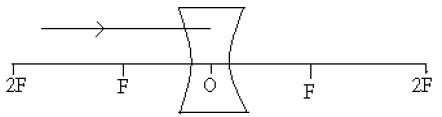
Q7. What is an oxidation reaction? Give an example of oxidation reaction. Is oxidation an exothermic or an endothermic reaction? [2]
Q8. A compound which is prepared from gypsum has the property of hardening when mixed with a proper quantity of water. Identify the compound. Write the chemical equation for its preparation. For what purpose is it used in hospitals? [2]
Q9. A wire is 1.0 m long, 0.2 mm in diameter and has a resistance of 10W. Calculate the resistively of its material. [2]
Q10. What is the minimum number of rays required for locating the image formed by a concave mirror for an object? Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror. [2]
Q11. Give reasons for the following observations: [3]
(a) The element carbon forms a very large number of compounds.
(b) Air holes of gas burner have to be adjusted when the heated vessels get blackened by the flame.
(c) Use of synthetic detergents causes pollution of water.
Q12. What is meant by ‘refining of metals’? Describe the electrolytic refining of copper with a neat labeled diagram. [3]
Q13. Two resistors, with resistances 10 ome and 15 ome are to be connected to a battery of emf 12 V so as to obtain.
(i) minimum current
(ii) maximum current
(a) Describe the mode of connecting the resistance in each case.
(b) Calculate the strength of the total current in the circuit in each case. [3]
Q14. What is hypermetropia? State the two causes of hypermetropia. With the help of ray diagram, show:
(i) the eye – defect hypermetropia
(ii) correction of hypermetropia by using a lens [3]
Q15. (a) Which two criteria did Mendeleev use to classify the elements in his periodic table?
(b) State Mendeleev’s periodic law.
(c) Why could no fixed position be given to hydrogen in Mendeleev’s periodic table?
(d) How and whey does the atomic size vary as you go:
(i) From left to right along a period?
(ii) Down a group? [5]
OR
(a) Why did Mendeleev have gaps in his periodic table?
(b) State any three limitations of Mendeleev’s classification.
(c) How do electronic configurations of atoms change in period with increase in atomic number? [5]
Q16. (a) What is magnetic field? How can the direction of magnetic field lines at a placed be determined?
(b) State the rule for the direction of the magnetic field produced around a current carrying conductor. Draw a sketch of the pattern of field lines due to a current flowing through a straight conductor. [5]
OR
(a) What is solenoid? Draw a sketch of the pattern of field lines of the magnetic field through and around a current carrying solenoid.
(b) Consider a circular loop of wire lying in the plane of the table. Let the current pas through the loop clockwise. Apply the right hand rule to find out the direction of the magnetic field inside and outside the loop. [5]
SECTION – B
Q17. Define ‘reflex action.’ [1]
Q18. What are the two main components of our environment? [1]
Q19. What will happen to a plant if its xylem is removed? [1]
Q20. What are ‘nastic’ and ‘curvature’ movements? Give one example of each. [2]
Q21. What is water harvesting? Mention any two water harvesting structures. [2]
Q22. Why must we conserve our forests? List any tow causes for deforestation taking place. [2]
Q23. (a) Distinguish between renewable and non – renewable sources of energy.
(b) Choose the renewable sources of energy from the following list:
Coal, biogas, sun, natural gas [2]
Q24. What is biogas? Why biogas is considered an ideal fuel for domestic use? [2]
Q25. What are sexually transmitted diseases? Name four such diseases. Which one of them damages the immune system of human body? [3]
Q26. Explain analogous organs and homologous organs. Identify the analogous and homologous organs amongst the following:
Wings of an insect, wings of a bat, forelimbs of frog, forelimbs of a human. [3]
Q27. (a) Draw a diagram of human alimentary canal and label on it: Oesophagus, gallbladder, liver and pancreas
(b) Explain the statement, ‘Bile does not contain any enzyme but is essential for digestion.’ [5]
OR
(a) draw a diagram of excretory system in human beings and label on it: [5]
Aorta, vena cava, urinary bladder, urethra.
(b) List two vital functions of the kidney.