Series OSS Code No. 56/1
CHEMISTRY (Theory)
Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70
General Instructions :
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Marks for each question are indicated against it.
(iii) Questions number 1 to 8 are very short-answer questions and carry 1 mark each.
(iv) Questions number 9 to 18 are short-answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
(v) Questions number 19 to 27 are also short-answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
(vi) Questions number 28 to 30 are long-answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
(vii) Use Log Tables, if necessary. Use of calculators is not allowed.
1. What type of interactions hold the molecules together in a polar molecular solid ? 1
2. What is meant by ‘limiting molar conductivity’ ?
3. Fluorine does not exhibit any positive oxidation state. Why ?
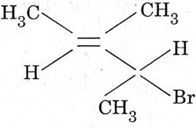
4. Give the IUPAC name of the following compound
5. Write the structure of the molecule of a compound whose IUPAC name
is
6. What is Tollen’s reagent ? Write one usefulness of this reagent.
7. What is meant by ‘reducing sugars’ ?
8. What does the designation ‘6, 6’ mean in the name nylon -6, 6 ?
9. Define the terms, ‘osmosis’ and ‘osmotic pressure’. What is the advantage of using osmotic pressure as compared to other colligative properties for the determination of molar masses of solutes in solutions ? 2
10. Express the relation among the cell constant, the resistance of the solution in the cell and the conductivity of the solution. How is the conductivity of a solution related to its molar conductivity ? 2
11. Given that the standard electrode potentials (E°) of metals are: ![]() ,
,
![]() .
.
Arrange these metals in an increasing order of their reducing power. 2
OR
Two half-reactions of an electrochemical cell are given below ![]()
Construct the redox reaction equation from the two half-reactions and calculate the cell potential from the standard potentials and predict if the reaction is reactant or product favoured. 2
12. Describe the following : 2
(i) Tyndall effect
(ii) Shape-selective catalysis
13. What is meant by coagulation of a colloidal solution ? Name any method by which coagulation of lyophobic sols can be carried out. 2
14. Complete the following chemical reaction equations : 2
(i) ![]()
(conc.)
(ii) ![]()
15. Draw the structural formulae of the following compounds : 2
(i) ![]()
(ii) ![]()
16. Give the chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds 2
(i) Ethylamine and Aniline
(ii) Aniline and Benzylamine
17. Identify A and B in each of the following processes 2
(i). ![]()
(ii). ![]()
18. Draw the molecular structures of the monomers of 2
(i) PVC
(ii) Teflon
19. The density of copper metal is 8.95 g cm 3. If the radius of copper atom be 127.8 pm, is the copper unit cell simple cubic, body-centred cubic or face-centred cubic ? (Given : atomic mass of Cu = 63.54 g mol-1 and ![]() = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1) 3
= 6.02 x 1023 mol-1) 3
20. What mass of NaCl (molar mass = 58.5 g mol-1) must be dissolved in 65 g of water to lower the freezing point by 7.5° C ? The freezing point depression constant, ![]() , for water is 1.86 K kg mol-1. Assume van’t Hoff factor for NaCl is 1.87. 3
, for water is 1.86 K kg mol-1. Assume van’t Hoff factor for NaCl is 1.87. 3
21. Describe the role of the following 3
(i) NaCN in the extraction of silver from a silver ore
(ii) Iodine in the refining of titanium
(iii) Cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium
OR
Describe the principle involved in each of the following processes of metallurgy : 3
(i) Froth floatation method
(ii) Electrolytic refining of metals
(iii) Zone refining of metals
22. Explain the following cases giving appropriate reasons : 3
(i) Nickel does not form low spin octahedral complexes.
(ii) The ∏-complexes are known for the transition metals only.
(iii) Co2+ is easily oxidised to Co3+ in the presence of a strong ligand.
23. How would you differentiate between ![]() mechanisms of substitution reactions ? Give one example of each. 3
mechanisms of substitution reactions ? Give one example of each. 3
24. How would you convert the following 3
(i) Phenol to benzoquinone
(ii) Propanone to 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(iii) Propene to propan-2-ol
25. How would you account for the following : 3
(i) ![]() is an endothermic compound while
is an endothermic compound while ![]() is an exothermic one.
is an exothermic one.
(ii) ![]() is a linear molecule without a bend.
is a linear molecule without a bend.
(iii) The electron gain enthalpy with negative sign for fluorine is less than that for chlorine, still fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent than chlorine.
26. Amino acids may be acidic, alkaline or neutral. How does this happen ? What are essential and non-essential amino acids ? Name one of each type. 3
27. Explain the following terms with one example in each case : 3
(i) Food preservatives
(ii) Enzymes
(iii) Detergents
28. (a) Explain the following terms
(i) Rate of a reaction
(ii) Activation energy of a reaction
(b) The decomposition of phosphine, ![]() , proceeds according to the following equation :
, proceeds according to the following equation :
![]()
It is found that the reaction follows the following rate equation :
Rate = k [![]() ].
].
The half-life of PH3 is 37.9 s at 120° C.
(i) How much time is required for ¾th of ![]() to decompose ?
to decompose ?
(ii) What fraction of the original sample of ![]() remains behind after 1 minute ? 5
remains behind after 1 minute ? 5
OR
(a) Explain the following terms
(i) Order of a reaction
(ii) Molecularity of a reaction
(b) The rate of a reaction increases four times when the temperature changes from 300 K to 320 K. Calculate the energy of activation of the reaction, assuming that it does not change with temperature. (R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1) 5
29. (a) Complete the following chemical equations
(i) ![]()
(ii) ![]()
(b) How would you account for the following
(i) The oxidising power of oxoanions are in the order
(ii) The third ionization enthalpy of manganese (Z = 25) is exceptionally high.
(iii) Cr2+ is a stronger reducing agent than Fee+. 5
OR
(a) Complete the following chemical equations
(i) ![]()
(ii) ![]()
(b) Explain the following observations
(i) La3+ (Z = 57) and Lu3+ (Z = 71) do not show any colour in solutions.
(ii) Among the divalent cations in the first series of transition elements, manganese exhibits the max. paramagnetism.
(iii) Cu+ ion is not known in aqueous solutions. 5
30. (a) Illustrate the following name reactions giving a chemical equation in each case :
(i) Clemmensen reaction
(ii) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(b) Describe how the following conversions can be brought about
(i) Cyclohexanol to cyclohexan-1-one
(ii) Ethylbenzene to benzoic acid
(iii) Bromobenzene to benzoic acid 5
OR
(a) Illustrate the following name reactions
(i) Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction
(ii) Wolff Kishner reduction reaction
(b) How are the following conversions carried out
(i) Ethylcyanide to ethanoic acid
(ii) Butan-1-ol to butanoic acid
(iii) Methylbenzene to benzoic acid
Write chemical equations for the involved reactions. 5