Karnataka Board SSLC Exam Question Paper
Mathematics
June - 2009
General Instructions :
i) The question-cum-answer booklet contains two Parts, Part – A & Part – B.
ii) Part – A consists of 60 questions and Part – B consists of 16 questions.
iii) Space has been provided in the question-cum-answer booklet itself to answer the questions.
iv) Follow the instructions given in Part – A and write the correct choice in full in the space provided below each question.
v) For Part – B enough space for each question is provided. You have to answer the questions in the space provided.
vi) Space for Rough Work has been printed and provided at the bottom of each page.
PART – A
Four alternatives are suggested to each of the following questions / incomplete statements. Choose the most appropriate alternative and write the answer in the space provided below each question. 60 × 1 = 60
1. If U = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 } and A = { 0, 1, 3, 5, 7 } , then Al is
(A) { 0, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9 } (B) { 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 }
(C) { 2, 4, 6, 8 } (D) { 2, 4, 6, 8, 9 } .
2. If A and B are disjoint sets, then n ( A ∩ B ) is
(A) 0 (B) ϕ
(C) { 0 } (D) { ϕ } .
3. If A = { 1, 2, 3 } , B = { 0, 1, 3, 4 } and C = { 2, 3, 4 } , then the set A U ( B ∩ C )
represents
(A) { 0, 1, 2, 3 } (B) { 0, 1, 3, 4 }
(C) { 1, 2, 3, 4 } (D) { 2, 3, 4 } .
4. In a progression, if Tn = 2n2 + 1, then S2 is
(A) 9 (B) 12
(C) 10 (D) 11.
5. In an A.P., the common difference is 3, first term is 1, then its tenth term is
(A) 27 (B) 29
(C) 30 (D) 28.

7. If x, y, z are in H.P., then the harmonic mean is
(A) 2xz/x + z (B) 2xy/x + y
(C) 2yz/y + z (D) 2xz/x + y
8. If A, G, H are AM, GM and HM of a and b, then
(A) A, G, H are in A.P.
(B) A, G, H are in G.P.
(C) A, G, H are in H.P.
(D) A, G, H are not in any of A.P., G.P. and H.P.
9. In a G.P., T7 : T4 = 8 : 1, then common ratio r is
(A) 1 (B) 3
(C) 2 (D) 4.
10. If A is skew symmetric matrix, then which of the following is correct ?
(A) A = AI (B) A = – A
(C) AI = ( AI)I (D) A = – AI .

14. nPn-1 is
(A) ( n – 1 ) ! (B) ( n + 2 ) !
(C) n ! (D) ( n + 1 ) !.
15. If 11Pr = 990, then r is
(A) 3 (B) 4
(C) 2 (D) 5.
16. If nC9 = nC6 , then n is
(A) 3 (B) 15
(C) 10 (D) 14.
17. How many triangles can be formed by using 10 non-collinear points ?
(A) 100 (B) 110
(C) 120 (D) 140.
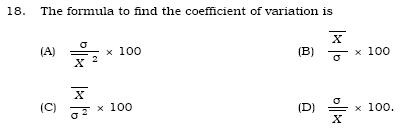
19. If ( 5x – 10 ) and (5x2 – 20) are two expressions, then their H.C.F. is
(A) 5 ( x – 2 ) (B) ( x – 2 )
(C) ( 5x – 2 ) (D) x – 10.
20. If A and B are two expressions and their H.C.F. is H, then their L.C.M. can be
calculated by using the formula
(A) L = (H × A)/B (B) L = A/(H × B)
(C) L = B/(A × H) (D) L = (A × B)/H .
21. H.C.F. and L.C.M. of two expressions are 5x2 y2 and 10x3 y3 respectively. If one
of the expressions is 5x 2 y 3 then other is
(A) 10x3 y3 (B) 10x2 y2
(C) 10x3 y2 (D) 5x3 y2.
22. When ∑ notation is used, the expression x2 + y2 + z2 – xy – yz – zx becomes
(A) ∑ x2 + ∑ xy (B) ∑ x2 – ∑ xy
(C) ∑ x2 – xy (D) ∑ x2 + xy.
23. When ∑ x ( y – z ) expanded and simplified, its value is
(A) 0 (B) xy – yz – zx
(C) xy – xz (D) xy + yz + zx.
24. If one of the factors of a3 – b3 is ( a – b ), then the other one is
(A) ( a2 + b2 – ab) (B) (a2 – b2 + ab)
(C) (a2 – b2 – ab) (D) (a2 + b2 + ab).
25. When a + b + c = 2s, then the value of ( b + c – a ) is
(A) 2s – a (B) 2 ( s – a )
(C) 2 ( s + a ) (D) 2s + a.
=================Please Go To Next Page================