PHYSICS - 2007 (A)
(Compulsory) - Science
Full Marks – 70 Time – 3 Hours
All questions are compulsory.
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable.
General Instructions :
(i). Question Nos. 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
(ii). Question Nos. 6 to 12 carry 2 marks each.
(iii). Question Nos. 13 to 24 carry 3 marks each.
(iv). Question Nos. 25 to 27 carry 5 marks each.
1. What is the SI unit of resistivity ?
2. What should be the orientation of a magnetic dipole in a uniform magnetic field so that its potential energy is maximum ?
3. What is photoelectric effect ?
4. What are the two functions performed by a modem ?
5. Arrange the following in ascending order of frequency :
Microwaves, γ-rays, Ultraviolet rays and Radiowaves.
6. State and explain Gauss’s theorem.
7. State Faraday’s laws of electrolysis.
8. The refractive index of glass is 3/2 and that of water is 4/3. If the speed of light in glass is 2.0 × (10)8 ms–1, what is the speed of light in water ?
9. What are the magnetic elements of earth at a place ? Define them.
10. Explain the working principle of AC generator.
11. What are the important characteristics of electromagnetic waves ?
12. Distinguish between the semiconductors and insulators.
13. A convex lens of focal length 25 cm and made of glass ( μg = 1.50) is immersed in water ( μw= 1.33). Find the change in the focal length of the lens.
14. The radius of first electron orbit of a hydrogen atom is 5.3 × (10)–11 m. What are the radii of the second and the third orbits ?
15. Two point charges of 5 nC and 20 nC are separated by a distance of 25 cm. Find the point on the line joining them at which electric field intensity is zero.
16. Derive the expression for the de-Broglie wavelength of an electron moving under a potential difference V.
17. Derive the expression for electric field at any point due to an electric dipole.
18. Draw the logic symbol of NOR gate and give its truth table.
19. Explain how a p-n junction diode can be used as a half-wave rectifier.
20. What are the functions of moderators and control rods in a nuclear reactor ?
21. State and explain Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction.
22. A series LCR circuit with R = 25 , L = 1.5 H and C = 30 μF is connected to a variable frequency 220 V a.c. supply. What is the average power transferred to the circuit in one complete cycle when the frequency of the supply equals the natural frequency of the circuit ?
23. Why sky wave propagation of electromagnetic waves cannot be used for TV transmission ? Suggest two methods by which range of TV transmissions can be increased.
24. Deduce an expression for the distance up to which the TV signals can directly be received from a TV tower of height h.
25. What are Kirchhoff’s rules for an electric circuit ? Apply the rules to obtain the balance condition of a Wheatstone’s bridge.
26. Describe, with theory, the construction and working of a moving coil galvanometer.
27. With the help of ray diagram, explain the formation of image in a compound microscope. Derive an expression for its magnifying power when the image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision.
CHEMISTRY - 2007 (A)
(Compulsory) - Science
Full Marks – 70 Time – 3 Hours
All questions are compulsory.
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable.
General Instructions :
(i). Question Nos. 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
(ii). Question Nos. 6 to 12 carry 2 marks each.
(iii). Question Nos. 13 to 24 carry 3 marks each.
(iv). Question Nos. 25 to 27 carry 5 marks each.
1. What is the space lattice of CaF2 ? 1
2. What is the rate of reaction with respect to A and B reacting species for the reaction 3A → 2B ? 1
3. Write IUPAC name of the compound. 1
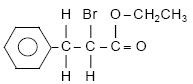
4. Why lower amines are soluble in water ? 1
5. State Roult’s law for solution of non-volatile solute. 1
6. Match the entries of the columns : 4× 1/2=2
Compound Bond

7. Give the equation to show the relation between equilibrium constant (K) and standard free energy change (![]() G°). Name all the terms involved in the equation. 1+1=2
G°). Name all the terms involved in the equation. 1+1=2
8. Write reaction and conditions for the following conversions : 1×2=2
(a) Benzene to Phenol
(b) Methanol to Ethanol
9. (a) Give the IUPAC name of the following : 1
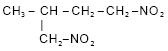
(b) How will you convert chlorobenzene into aniline ? 1
10. Give the possible value of quantum numbers for an electron in 4d orbital. 2
11. How does diethyl ether react with the following ? 2
(i) PCl5 (ii) Hl
12. Give some examples of inter-halogen compounds. 2
13. On the basis of bond order, explain the stability of ![]() 3
3
14. Define half-life. Prove that half-life of a first order reaction is independent of the initial concentration of the reactant. 1+2=3
15. Arrange the following in order of increasing acidic strength : 3
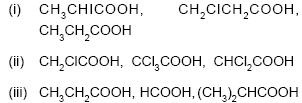
16. (a) Write the oxidation state of Ni in ![]() . 1(1/2)
. 1(1/2)
17. (a) In what respect does a double salt differ from coordination compound ? 2
(b) Write IUPAC name of ![]() 1
1
18. A solution of 12.5 g urea in 170 g of water gave a boiling point elevation of 0.63 K. Calculate the molecular weight of urea taking ![]() = 0.52 k/m. 3
= 0.52 k/m. 3
19. What do you understand by homogeneous catalyst ? Discuss the role of adsorption in catalysis. 1(1/2)+1(1/2)=3
20. Give the IUPAC names of the following : 1×3=3
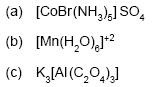
21. Bring out the following conversions : 1×3=3
(a) Acetaldehyde to Acetone
(b) Formaldehyde to Ethyl alcohol
(c) Acetic acid to Formaldehyde.
22. (a) Give two chemical methods for the preparation of colloids. 1(1/2)
(b) What happens when an electirc field is applied to a colloidal solution ? 1(1/2)
23. What are antibiotics ? Name any two antibiotics which are specific for certain diseases. 1+2=3
24. How does molar conductivity vary with concentration of a weak electrolyte in solution ? Discuss the significance of the Kohlrausch law. 1(1/2)+1(1/2)=3
25. How cast iron is extracted from Haematite ore ? 5
26. Suggest the hybridisation and shape of the following compounds and ions : 5

27. What are proteins ? Suggest, in brief, the different types of proteins. 5
Or
Discuss general characteristic of Group-14 elements.