Q. 1 (i) How do the layers of the Internet model correspond to the layers of the OSI model? (10 marks)
(ii) What is the difference between a port address, a logical address (IP address) and a physical address (as defined by LAN or WAN)? (10 marks)
(iii) Name some services provided by the application layer in the Internet model. (5 marks)
Answer:
(i) How do the layers of the Internet model correspond to the layers of the OSI model? (10 marks)
The TCP/IP model is quite different from the OSI model which is a conceptual model. The TCP/IP network architecture is a set of protocols that allow communication across multiple diverse networks. The architecture is an outcome of research that had the original objective of transferring packets across three different packet switched networks: the ARPANET packet-switching network, a packet radio network, and a packet satellite network.
Due to military application, the research focused on robustness and flexibility in operating over diverse networks and led to a set of protocols that are highly effective in having communications among the many different types of computer systems and networks. Today, the Internet has become the primary fabric for interconnecting the world's computers and the TCP/IP is the main protocol for carrying information.
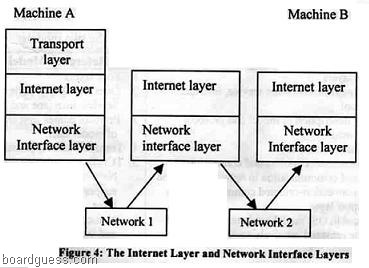
The Internet layer (Figure 4) is similar to the part of the OSI network layer that is concerned with the transfer of packets between machines that are connected to different networks through the use of gateways and routers. It must therefore deal with the routing of packets across these networks as well as with the control of congestion. The Internet layer also defines globally unique addresses for machines that are attached to the Internet. IP is a main protocol at this layer which provides a single service, namely, best-effort connectionless packet transfer. IP packets are exchanged between routers without a connection setup; the packets are routed independently, and so they may traverse different paths for the same destination. For this reason, IP packets are also called datagrams. The connectionless approach makes the system robust; which means that in the case of failures, there is no need to set up the connections. The gateways that interconnect the intermediate networks may discard packets when congestion occurs. The responsibility for recovery from these losses done by the transport layer.
Finally, the network interface layer is concerned with the network-specific aspects of the transfer of packets. As such, it must deal with parts equivalent to OSI network layer and data link layer. Various interfaces are available for connecting end computer systems to specific networks such as X.25, ATM, frame relay, Ethernet, and token ring.
(iii) Name some services provided by the application layer in the Internet model. (5 marks)
The application layer provides services that can be used by other applications such as remote login, e-mail, file transfer, and network management operations.
| Index Assignment || Next Answer>>